

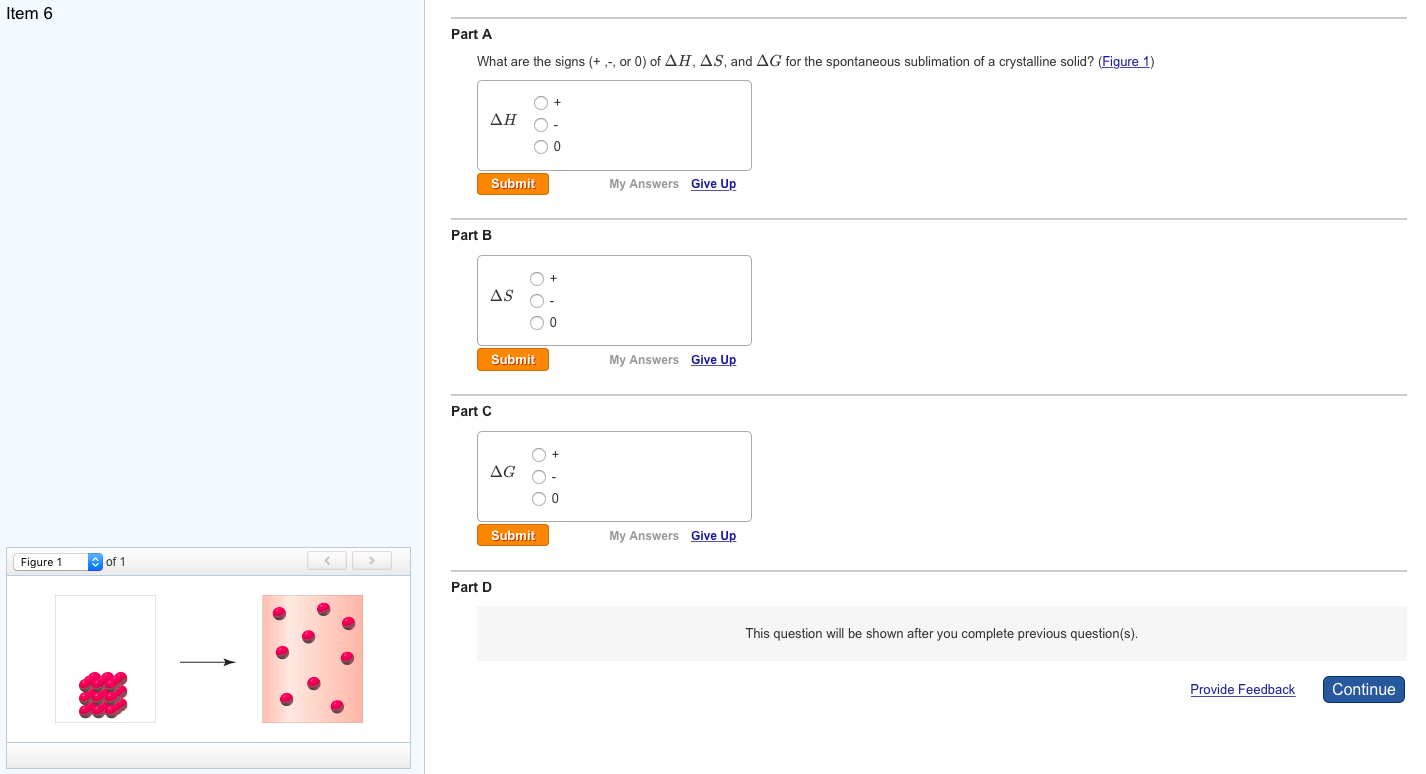
Calculate the temperature at which the reaction becomes spontaneous. 2C (s) + O2 (g) - 2CO (g) Students also viewed. Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers A) For the reaction 4HCl (g) + O2 (g)->2H2O (g) + 2Cl2 (g) Delta H -114.4 kJ and Delta S -128.9 J/K The equilibrium constant for this reaction at 306. At 25 C, 298 K, the reduction of copper (I) oxide, H 58.1 k J, S 165 J / K, is nonspontaneous, G 8.9 k J. The change in enthalpy, Delta H, is equal to the sum of. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Predict the signs of delta S and delta H for the freezing of water into ice at 273 degrees.

For example, our desired reaction has C 2H 4 as a reactant, and only one reaction from our data has C 2H 4. Course 32K views Enthalpy Change Formula Enthalpy, H, is a thermodynamic property that describes the heat lost or gained in a system. Expert Answer 100 (1 rating) (a) 2 CH4 > C2H4 + 2 H2 Delta Hrxn Delta Hf (products) - Delta Hf (reactants) Delta Hf (C2H4) + 2 x Delta Hf (H2) - 2 x Delta Hf (CH4) 52. We will start by writing chemical reactions that put the correct number of moles of the correct substance on the proper side.
So you want to decrease the value of T.ΔH = −167.5 kJ\nonumber \] Why: the sign flips when you flip the equation, and the enthalpy number drops by 0.5 when you scale the reaction by 0.5. (1) Calculate the entropy change of the UNIVERSE when 2.075 moles of H 2 CO(g) react under standard conditions at 298.15 K.
When Delta H and Delta S are both negative: - spontaneous at low temperatures *Delta H is negative *TDeltaS is positive Again we want the number to be larger so that Delta G will be negative and the reaction will be spontaneous. Turn around your second input equation, and multiply it throughout by the factor (1/2): (2SO3 2SO2 + O2)0.5 -> SO3 SO2 + (1/2)O2 associated with delta H (+198.2)0.5. Consider the reaction H 2 CO(g) + O 2 (g)CO 2 (g) + H 2 O(l) for which delta H° -563.3 kJ and delta S° -140.5 J/K at 298.15 K. For elements it's always zero, even the o2 or the diatomics. It actually is a process going from its elements reforming that. For compounds, when we're talking of the delta H, it's a formation of that.
Delta h and delta s for o2 webook plus#
Boiling is only spontaneous at high temperatures * Delta H is positive *-TDelta S is negative - We want the negative number to be larger so the Delta G will be negative and the reaction will be spontaneous. So Hess's Law tells us that delta H of this reaction, the change in enthalpy of this reaction, is essentially going to be the sum of what it takes to decompose these guys, which is the minus heat of formations of these guys, plus what it takes to reform these guys over here. So if we have an element, elements have a delta H of zero, always. The chemical equation is: 2 NO 2 (g) -> N 2 O 4 (g) For this reaction, E is -54.72 kJ. We know if Delta G >0 reaction is non spontaneous We know if Delta G G). Get the detailed answer: the vaules of delta h and delta s rxn for the reaction 2 NO(g)+O2(g) -> 2 NO2(g) are -147 j/k and -12.0 kj.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
